Configure Snowflake Connection Details (as data source)
Snowflake is a fully-managed SaaS data platform that provides features such as data warehousing, data lake, data science, data application development among many others. Snowflake provides out-of-the-box features like scalable computing, separation of storage and compute, data sharing, data cloning, and support for third-party tools to handle the demanding needs of businesses.
You can use Snowflake in different stages of a data pipeline in the Calibo Accelerate platform:
-
To use Snowflake as a data lake in your data pipelines or in your data transformation and data quality stages, see Configure Snowflake as a Data Lake.
-
To use Snowflake as a data source in a data ingestion pipeline, configure your Snowflake connection details in the RDBMS section of Databases and Data Warehouses. See Configure Snowflake as a Data Source.
The Calibo Accelerate platform offers various options for retrieving your database credentials to establish a secure connection. You can either directly provide the credentials within the connection details, where they are securely stored in the Calibo-managed secret manager. Alternately, you can choose to retrieve credentials programmatically from your designated secrets management tool.
Note:
The user that you configure must have the read-only access to your RDBMS.
To configure the connection details of Snowflake as a data source, do the following:
- Sign in to the Calibo Accelerate platform and click Configuration in the left navigation pane.
- On the Platform Setup screen, on the Cloud Platform, Tools & Technologies tile, click Configure.
- On the Cloud Platform, Tools & Technologies screen, in the Databases and Data Warehouses section, click Configure.
(After you save your first connection details in this section, you see the Modify button here.)
-
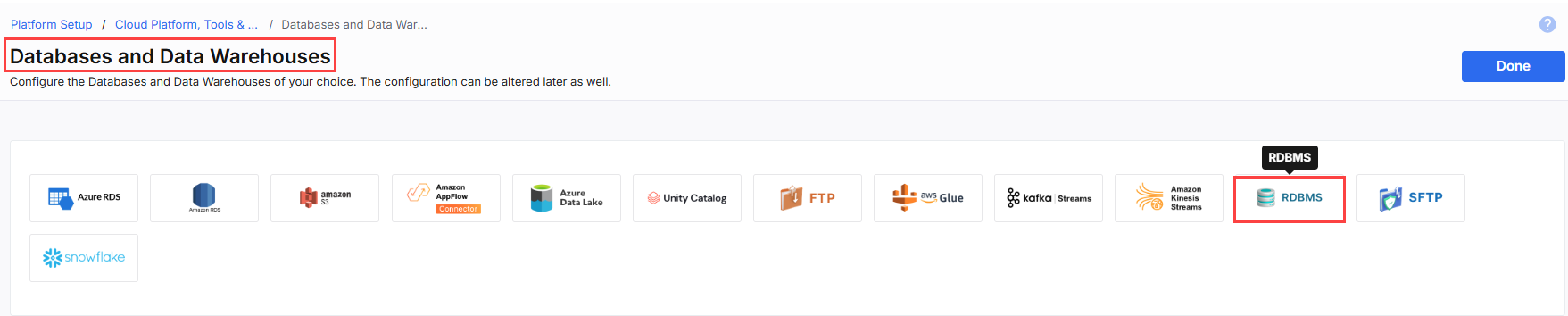
In the list of available Databases and Data Warehouses, click
 .
. 
- On the RDBMS screen, do the following:
In the Details section, provide the following information:
Field Description Name Give a unique name to your Snowflake configuration. This name is used to save and identify your specific Snowflake connection details within the Calibo Accelerate platform. Description Provide a brief description that helps you identify the purpose or context of this Snowflake configuration.
-
In the Configuration section, do the following:
- From the RDBMS Subtype, select Snowflake.
- Provide the Account URL for your Snowflake account.
- Select Cloud Provider - Select the cloud platform on which your Snowflake account is hosted. Choose from the following options:
- AWS
- Azure
-
Depending on how you want to retrieve the credentials to connect to Snowflake, do one of the following:
Field Description Connect using Calibo Accelerate Orchestrator Agent Enable this option to resolve your Snowflake credentials within your private network via Calibo Accelerate Orchestrator Agent without sharing them with the Calibo Accelerate platform.
Select the Calibo Accelerate Orchestrator Agent that you want to use from the list of your configured agents.
-
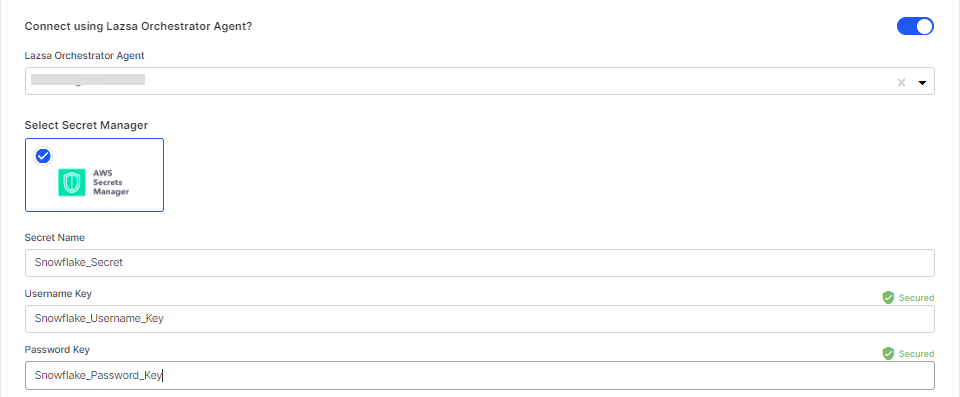
If you select an agent installed in an Amazon EKS cluster, the secrets management tool AWS Secrets Manager is auto-selected. Provide the Secret Name using which you store your Snowflake credentials. Provide the Username Key and Password Key.
-
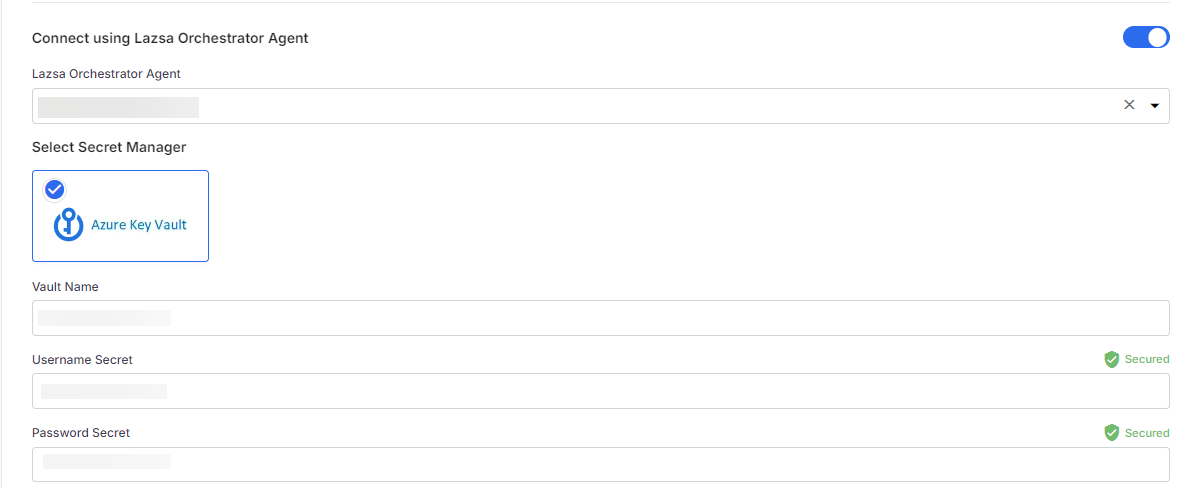
If you select Azure as the cloud provider in the above step, the dropdown list shows a list of Azure agents installed in an AKS cluster. The secrets management tool Azure Key Vault is auto-selected. Provide the Vault Name, Username Secret, and Password Secret of the secret where you store your Snowflake credentials.
Select Secret Manager - Select Calibo Accelerate and type your Snowflake Username and Password.

In this case, the user credentials are securely stored in the Calibo-managed secrets store.
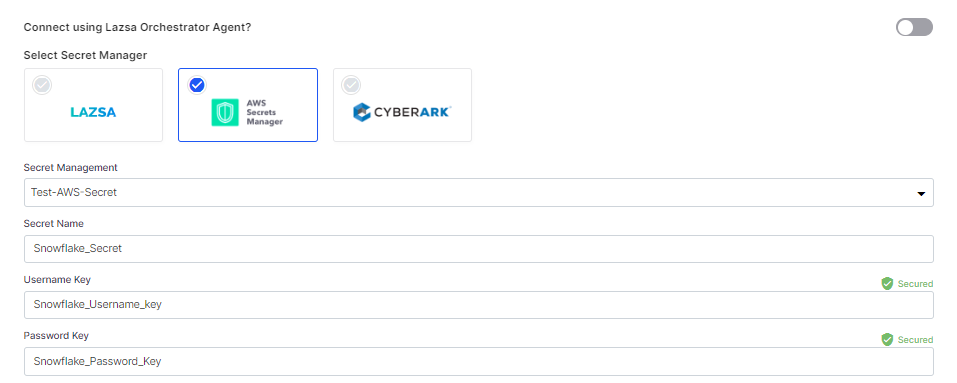
- Select AWS Secrets Manager. In the Secret Management dropdown list, the AWS Secrets Manager configurations that you save and activate in the Secret Management section on the Cloud Platform, Tools & Technologies screen are listed for selection. Select the configuration of your choice. Provide the Secret Name, Username Key, and the Password Key for the Calibo Accelerate platform to retrieve the secrets for your Snowflake account.
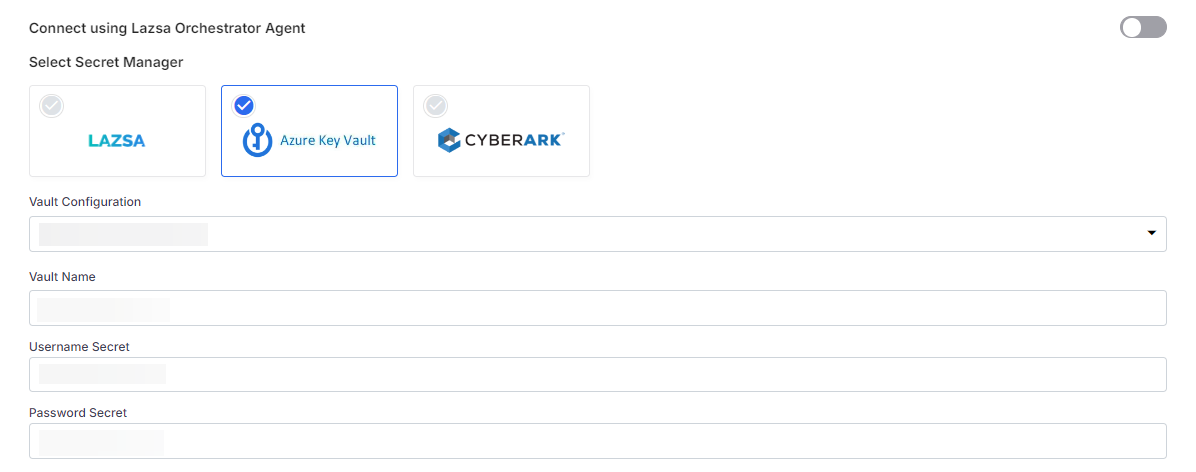
- Select Azure Key Vault. In the Vault Configuration dropdown list, the Azure Key Vault configurations that you save and activate in the Secret Management section on the Cloud Platform, Tools & Technologies screen are listed for selection. Select the Vault Configuration of your choice. Provide the Vault Name, Username Secret, and Password Secret for the Calibo Accelerate platform to retrieve the credential values.
-
- Click Test Connection to validate whether you have configured the correct connection details and you can connect to Snowflake successfully.
- Database - Select a database from the dropdown list of configured databases in your Snowflake account.
- Schema - Select a schema from the list of schemas that are part of the selected database.
- Warehouse - Select a warehouse for the database. You can either select an existing warehouse or create a new warehouse. See Create Snowflake Warehouse.
- View Details - Click to view the configuration details of the Snowflake warehouse that you selected from the dropdown list.
- (...) - click the ellipsis to edit, resume, or delete a warehouse.
- Secure configuration details with a password
To password-protect your Snowflake connection details, turn on this toggle, enter a password, and then retype it to confirm. This is optional but recommended. When you share the connection details with multiple users, password protection helps you ensure authorized access to the connection details. -
Click Save Configuration. You can see the configuration listed on the Databases and Data Warehouses screen as an RDBMS Snowflake connection.
|
What's next? Data Visualization |