Ingesting Data using Snowflake Bulk Ingest into a Snowflake Data Lake
In big data processing, sometimes it is required to load huge amounts of data in batches. In this scenario, bulk ingestion is extremely useful. Snowflake Bulk Ingest when used in the data integration stage, helps you load batches of data from files available in a data lake like Amazon S3. Bulk Ingest loads chunks of data every time you run the pipeline. Data is first pushed into a landing layer, and then sent to the unification layer.
Calibo's Data Pipeline Studio (DPS) supports bulk ingestion of data using Snowflake bulk ingest in the data integration stage, S3 as data lake in the data source stage, and Snowflake as the target data lake. Following is an example of a Snowflake bulk ingest data pipeline:
How Snowflake Bulk Ingest works
In case of Snowflake bulk ingest, every time you run the data pipeline, data from S3 is ingested into the data lake. During data ingestion, the data is first pushed into a landing layer. Depending on the use case, you can perform operations like append, overwrite or merge on the data. The processed data is then pushed into the unification layer. During this process credentials are required to access the Amazon S3 bucket. Read, write permissions are required to Snowflake objects. You can avoid sharing credentials directly and instead use Storage Integration.
What is Storage Integration?
Storage Integration is a Snowflake object that helps you to connect to the AWS account from Snowflake using the IAM service. You can specify allowed and blocked storage locations. This way you can provide enhanced security to the complete data ingestion operation.
See Configuring a Snowflake storage integration to access Amazon S3.
Prerequisites for using Snowflake Bulk Ingest in the data integration layer
Ensure that you meet the following prerequisites:
-
You must have Amazon S3 and Snowflake data lake configured in the Calibo Accelerate platform.
-
You must have a storage integration created in Snowflake.
To create a data integration job for Snowflake bulk ingest
-
On the home page of DPS, add the following stages. Your pipeline looks like this:
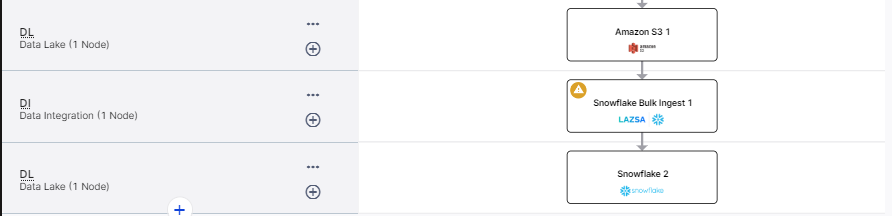
-
Data Lake: Amazon S3
-
Data Integration: Snowflake Bulk Ingest
-
Data Lake: Snowflake
-
-
Configure the Amazon S3 and Snowflake nodes.
-
Click on the data integration node and click Create Job.
-
For the data integration job creation, provide the following inputs:
-
Job Name: Provide a name for the data integration job.
-
Node Rerun Attempts: This is the number of times the pipeline run is attempted on this node in case of failure. By default the setting done at the pipeline level is considered. To change the default setting, you can select an option from the dropdown.
-
Fault tolerance - Select the behaviour of the pipeline upon failure of a node. The options are:
-
Default - Subsequent nodes should be placed in a pending state, and the overall pipeline should show a failed status.
-
Skip on Failure - The descendant nodes should stop and skip execution.
-
Proceed on Failure - The descendant nodes should continue their normal operation on failure.
-
-
Datastore: This is populated based on the datastore that you configure for the data lake (source) node.
-
Source Format: The supported format is Parquet. This format is pre-selected and the field is non-editable.
-
Choose Base Path:
-
Click Add Base Path.
-
In the Choose Base Path screen, select a path and then click Select.
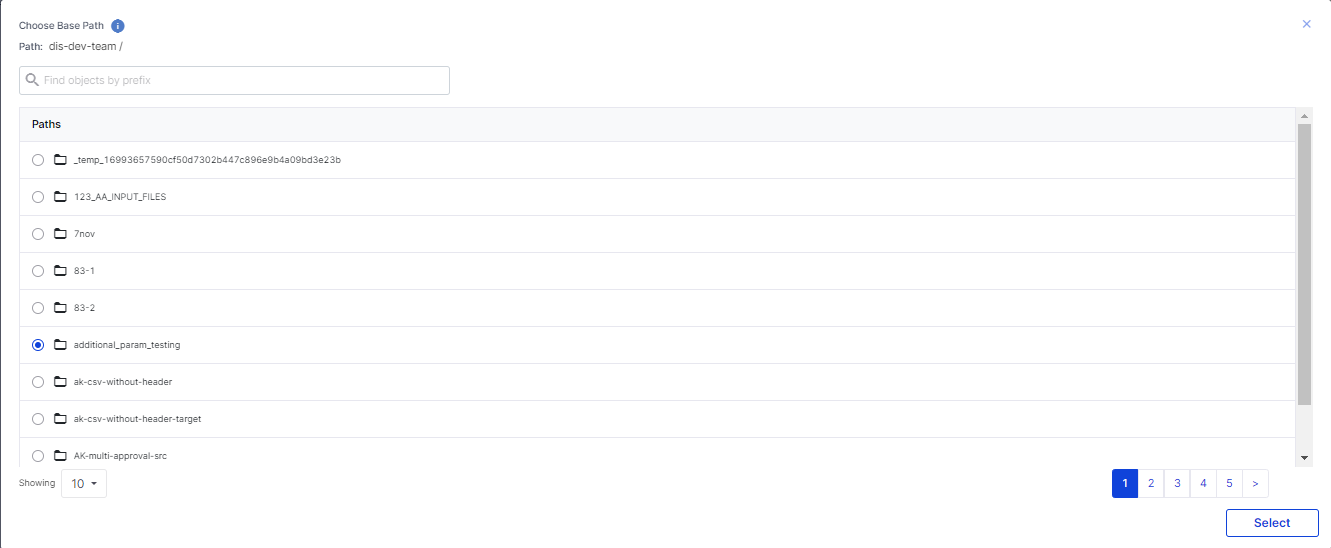
Click Next.
-
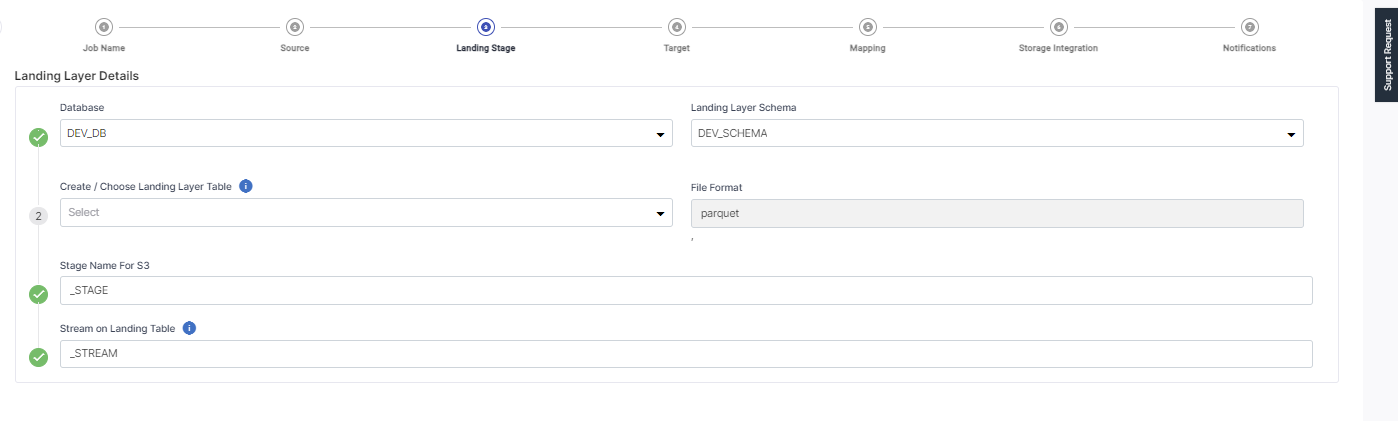
On the Landing Layer Details screen, provide the following inputs:
-
Database – This is populated based on the selected database.
-
Landing Layer Schema – This is populated based on the selected schema.
-
Create/Choose Landing Layer Table – Either select a table from the dropdown list or create a new table in the landing layer where the data is stored temporarily.
-
Choose File Format – This is populated based on the file format that you selected for the source stage.
-
Stage Name for S3 – This is created based on the landing layer table that you create or choose. A suffix Stage is added to it to form the stage name for S3.
-
Stream on Landing Table – This is created based on the landing layer table that you create or choose. A suffix Stream is added to it to form the Stream name for the landing table.
-
Click Next.
The Datastore is populated based on the options selected.
Provide the following information for Unification Layer Details:
-
Warehouse - Select a warehouse to store the data.
-
Database - This is populated based on the selected database.
-
Target Schema - This is populated based on the selected schema.
-
Create/Choose Unification Layer Table - Either select a table from the dropdown list or create a new table in the unification layer where the data is stored temporarily.
-
Operation Type: Select the type of operation to be performed on the source data during the job run. Choose one of the following options:
-
Append - adds new data at the end of the table without erasing the existing content.
-
Overwrite – replaces the existing data in the table.
-
Merge – combines the existing and new data in the table. Select a primary key based on which the data merge is done.
-
This screen lets you map the columns and datatypes from the selected source table with the columns and data types in the target table.
-
Handle special characters in column names - This section lets you handle special characters in column names in the following two ways:
-
Enclose text with special characters in double quotes (" ").
-
Replace special characters in text with underscore (_).
-
-
Enable Add Custom Columns to add additional custom columns to the target table as per your requirement, and provide the following information:
-
Column Name – Provide a name for the custom column.
-
Type – Select from static parameter or system parameter. For static parameter provide a value. For system parameter, select a parameter value from the dropdown list.
-
Value – Provide a value or select one from the dropdown depending on the type you select.
-
Click Add.
Under Added Custom Columns, you can perform the following actions:
-
Click the pencil icon to edit the details of the custom column. Make the required changes and click Update.
-
Delete the custom column that you have added by clicking the Delete icon.
Select a storage integration from the dropdown list.
A storage integration is an object created in Snowflake that stores a generated identity and access management (IAM) user for your S3 cloud storage, along with an optional set of allowed or blocked storage locations (i.e. buckets).
Ensure that the storage integration that you select has access to the selected S3 bucket in the source stage.
For information on how to create a storage integration, refer to the following link:
Configuring a Snowflake storage integration to access Amazon S3.
You can configure the SQS and SNS services to send notifications related to the node in this job. This provides information about various events related to the node without actually connecting to the Calibo Accelerate platform.
| SQS and SNS |
|---|
| Configurations - Select an SQS or SNS configuration that is integrated with the Calibo Accelerate platform. |
|
Events - Enable the events for which you want to enable notifications:
|
| Event Details - Select the details of the events from the dropdown list, that you want to include in the notifications. |
| Additional Parameters - Provide any additional parameters that are to be added in the SQS and SNS notifications. A sample JSON is provided, you can use this to write logic for processing the events. |
| `What's next?Ingesting Data using Snowflake Stream Ingest into a Snowflake Data Lake |