Custom Integration with target as Amazon S3 Data Lake
The Calibo Accelerate platform now provides the option to write custom code in order to read data from a supported data source and ingest it into an Amazon S3 data lake. Apart from templatized integration jobs, you can now perform complex operations on data, by creating custom integration jobs.
| Source | Custom Integration | Data Lake |
|---|---|---|
| RDBMS - MySQL | Databricks | S3 |
| RDBMS - Oracle Server | Databricks | S3 |
| RDBMS - Microsoft SQL Server | Databricks | S3 |
| RDBMS - PostgreSQL | Databricks | S3 |
| RDBMS - Snowflake | Databricks | S3 |
| FTP | Databricks | S3 |
| SFTP | Databricks | S3 |
| REST API | Databricks | S3 |
| Azure Data Lake | Databricks | S3 |
| Amazon S3 | Databricks | S3 |
To create a Databricks custom integration job
-
Sign in to theCalibo Accelerate platform and navigate to Products.
-
Select a product and feature. Click the Develop stage of the feature, you are navigated to Data Pipeline Studio.
-
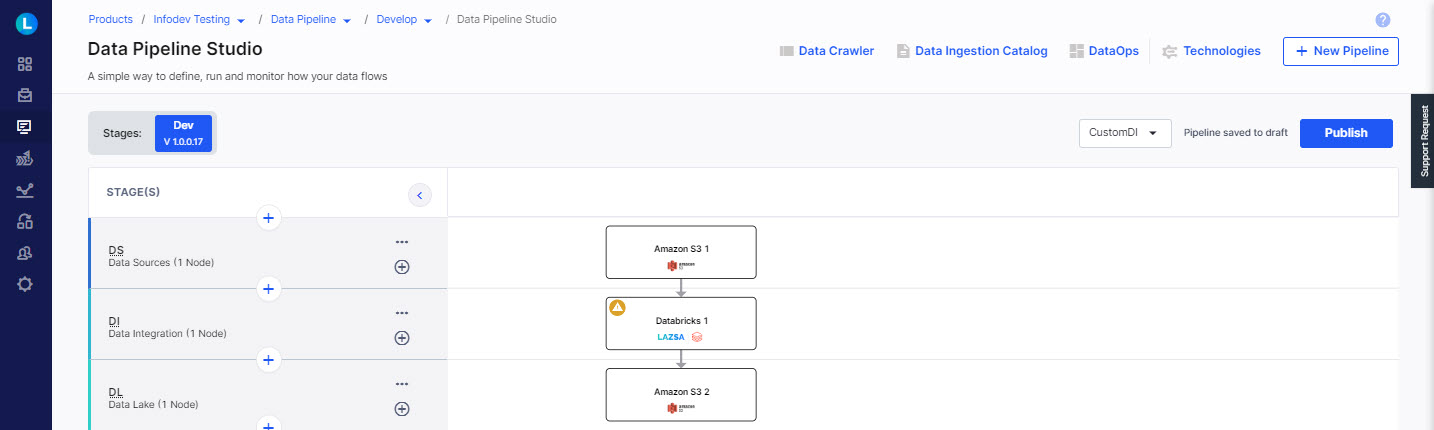
Create a pipeline with the following nodes:
Note: The stages and technologies used in this pipeline are merely for the sake of example.
-
Data Source - Amazon S3
-
Data Integration- Databricks
-
Data Lake - Amazon S3
-
-
Configure the Amazon S3 nodes in the data source and data lake stages.
-
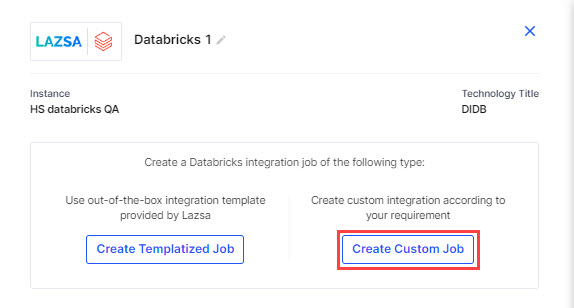
In the data integration stage click the Databricks node, and select Create Custom Job - to create a custom integration job.
-
Complete the following steps to create the Databricks custom integration job:
 Job Name
Job Name
Provide job details for the data transformation job:
-
Job Name - provide a name for the data integration job that you are creating.
-
Node Rerun Attempts - this is the number of times the pipeline rerun is attempted on this node, in case of failure. The default setting is done at the pipeline level. You can select rerun attempts for this node. If you do not set the rerun attempts, then the default setting is considered.
-
Fault tolerance - Select the behaviour of the pipeline upon failure of a node. The options are:
-
Default - Subsequent nodes should be placed in a pending state, and the overall pipeline should show a failed status.
-
Skip on Failure - The descendant nodes should stop and skip execution.
-
Proceed on Failure - The descendant nodes should continue their normal operation on failure.
-
Click Next.
-
-
Click Configure Branch Template. You are navigated to the Develop stage of the feature in which the pipeline is created. Click Configure.
-
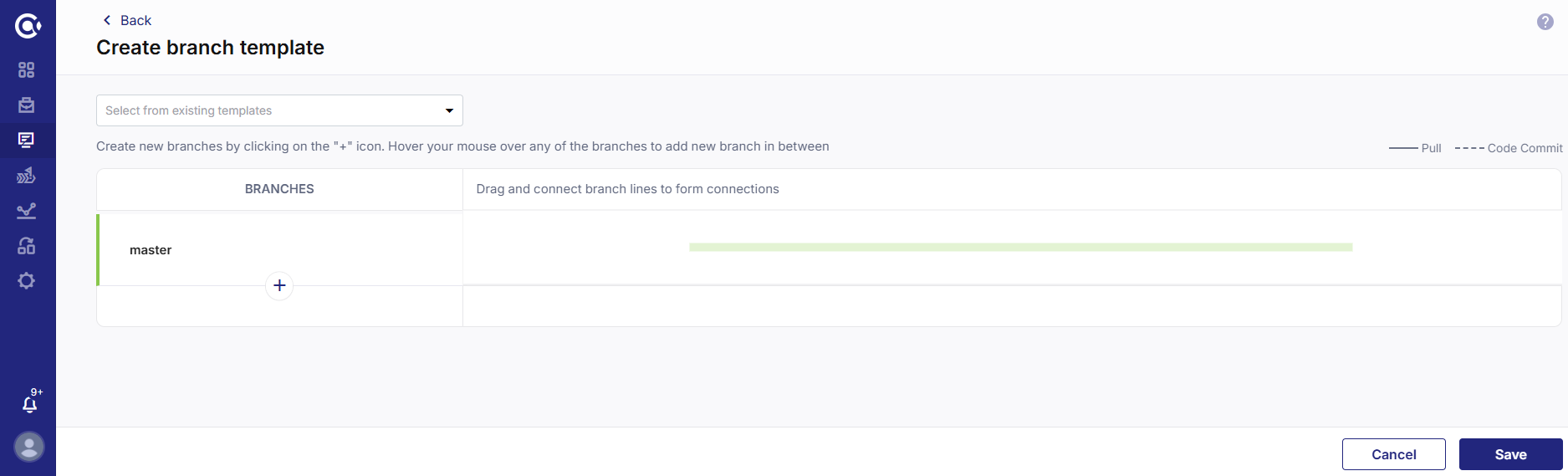
On the Create Branch Template screen do one of the following:
-
Select an existing template from the dropdown list and add or delete the required branches.
-
Click + (Add New Branch) and create branches as per your requirement.
-
-
Click Save.
-
Create a new repository. Provide the following information:
-
Repository Name - A repository name is provided in the default format. The repository name is populated in the following format: Technology Name - Product Name. For example if the technology being used is Databricks and the product name is ABC, then the repository name is Databricks-ABC. You can edit this name to create a custom name for the repository.

Note:
You can edit the repository name when you use the instance for the first time. Once the repository name is set, you cannot change it thereafter.
-
Group - Select a group to which you want to add this repository. Groups help you to organize, manage, and share the repositories for the product.
-
Visibility - Select the type of visibility that the repository must have. Choose from Public or Private.
-
-
Click Create Repository. Once the repository is created, the Repository path is displayed.
-
Select the Source Code Branch.
-
-
Use Existing Repository - Enable the toggle to use an existing repository. Provide the following information:
-
Title - The technology title is added.
-
Repository Name - Select a repository from the dropdown list.
-
-
System Defined Parameters - Deselect the parameters that you do not want to include with the transformation job and click Next.
-
Custom Parameters - You can either add custom parameters manually or you can import them from a JSON file.
-
Add Manually - Provide a key and value. Mark the parameter as Sensitive or Mandatory depending on your requirement.
-
Import from JSON - You can download a template and create a JSON file with the required parameters or upload a JSON file directly.
-
-
Spot
-
On-demand
-
Spot with fallback
In this step, you can configure the branch template and the source code repository. This helps you to define your branch template and create the branches in the source code repository accordingly.
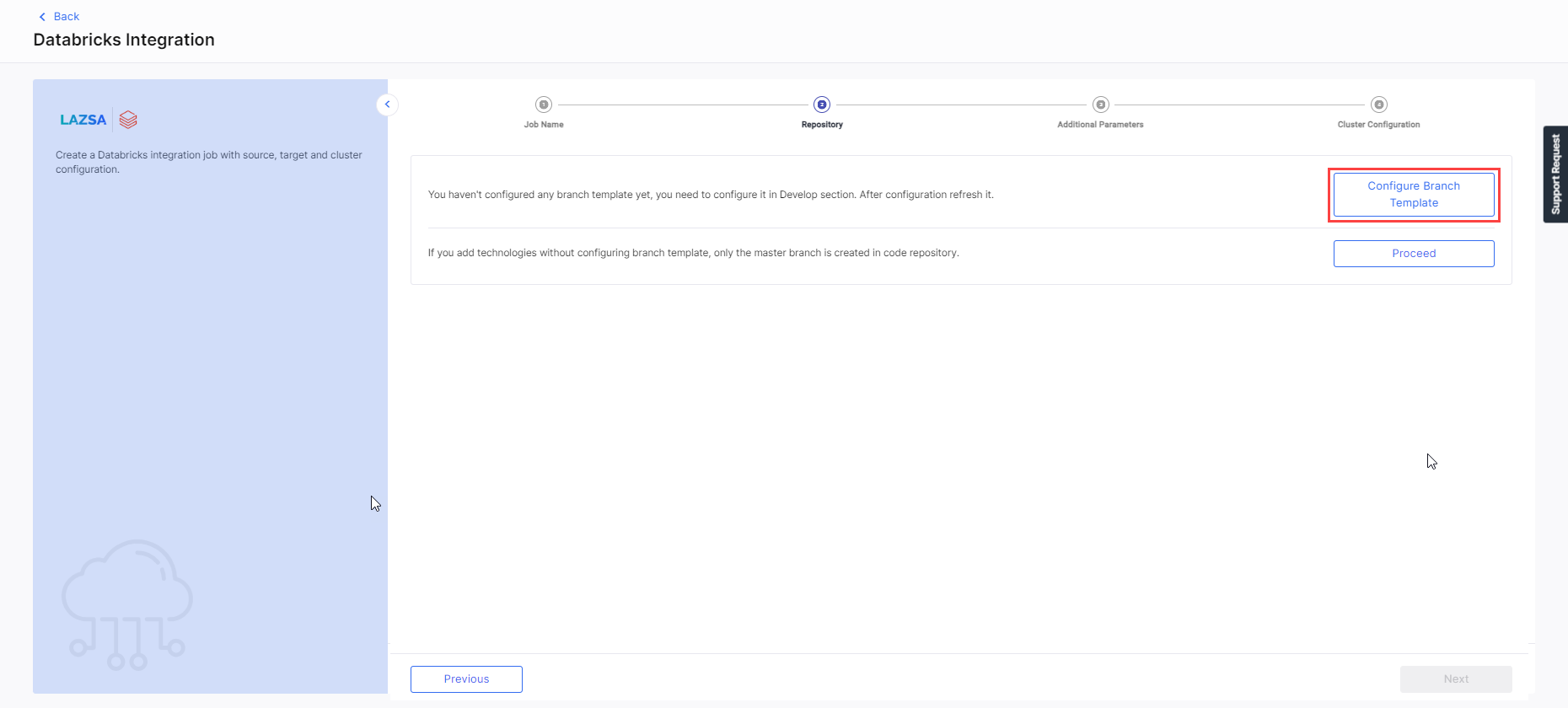
To configure branch template
To configure source code repository
You have the following two options to configure source code repository:
Click Next.
In this step, you can either provide system-defined parameters or custom parameters to the transformation job.
Click Next.
You can select an all-purpose cluster or a job cluster to run the configured job. Since you are creating a custom transformation job, you may require certain library versions for successfully running the transformation job. To update the library versions, see Updating Cluster Libraries for Databricks
In case your Databricks cluster is not created through the Calibo Accelerate platform and you want to update custom environment variables, refer to the following:
Updating Custom Variables for a Databricks Cluster
Cluster - Select an all-purpose cluster from the dropdown list, that you want to use for the data transformation job.
| Cluster Details | |
|---|---|
| Choose Cluster | Provide a name for the job cluster that you want to create. |
| Job Configuration Name | Provide a name for the job cluster configuration. |
| Databricks Runtime Version | Select the appropriate Databricks version. |
| Worker Type | Select the worker type for the job cluster. |
| Workers |
Enter the number of workers to be used for running the job in the job cluster. You can either have a fixed number of workers or you can choose autoscaling. |
| Enable Autoscaling | Autoscaling helps in scaling up or down the number of workers within the range specified by you. This helps in reallocating workers to a job during its compute-intensive phase. Once the compute requirement reduces the excess number of workers are removed. This helps control your resource costs. |
| Cloud Infrastructure Details | |
| First on Demand | Lets you pay for the compute capacity by the second. |
| Availability |
Select from the following options: |
| Zone | Select a zone from the available options. |
| Instance Profile ARN | Provide an instance profile ARN that can access the target S3 bucket. |
| EBS Volume Type | The type of EBS volume that is launched with this cluster. |
| EBS Volume Count | The number of volumes launched for each instance of the cluster. |
| EBS Volume Size | The size of the EBS volume to be used for the cluster. |
| Additional Details | |
| Spark Config | To fine tune Spark jobs, provide custom Spark configuration properties in key value pairs. |
| Environment Variables | Configure custom environment variables that you can use in init scripts. |
| Logging Path (DBFS Only) | Provide the logging path to deliver the logs for the Spark jobs. |
| Init Scripts | Provide the init or initialization scripts that run during the start up of each cluster. |
To replace the placeholder custom code
After you have created the custom integration job, click the Databricks Notebook icon. This navigates you to the custom integration job in the Databricks UI. Replace the code with your custom code and then run the job.
| What's next? Databricks Templatized Data Integration Jobs |